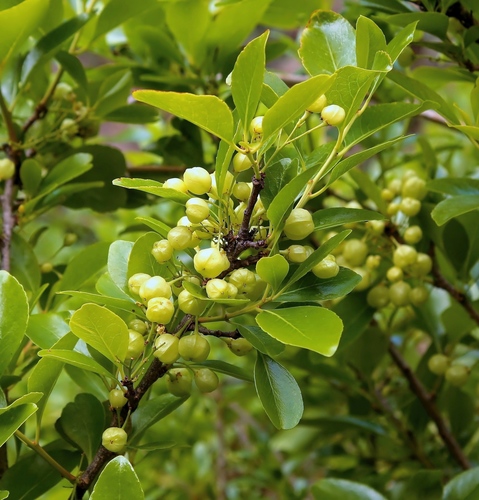
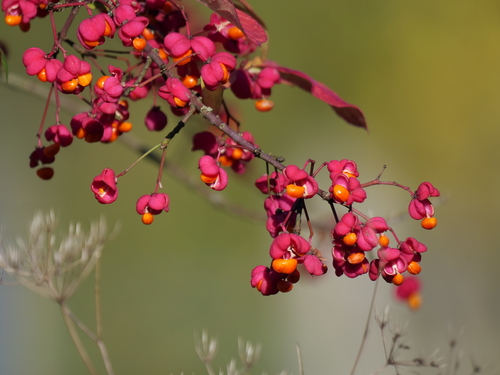Winged Spindle Tree
euonymus atropurpureus
Also known as: ["American Spindle","Winged Euonymus"]
Overview
A deciduous shrub or small tree native to eastern North America, known for its winged stems and showy pinkish-red fruits.
Benefits & Perks
["wildlife attractant (bees, butterflies, birds)","seasonal color change"]
Botanical Classification
| Phylum: | Magnoliophyta |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida |
| Order: | Celastrales |
| Family: | Celastraceae |
| Genus: | Euonymus |
| Botanical Name: | Euonymus atropurpureus |
Plant Characteristics
Basic Information
- Category: Shrubs
- Suitable Location: outdoor garden, adaptable to various soil types
- Suitable For:
- Is Weed: No
- Allergenicity: low
Environmental Needs
- Climate: {"temperatureRange":"–29 to 43°C"}
- Hardiness: {"zones":"3–8"}
- Misting: rarely required
- Drainage: Moderate to fast-draining; avoid heavy clay soils.
- Soil Type: Well-draining, loamy soil with organic matter; tolerates average garden soil.
Maintenance Level
- Maintenance Level: moderate
- Toughness Level: moderate
- Pruning Frequency: Annually in late winter or early spring; light pruning can be done after flowering.
- Pruning Intensity: Moderate; remove up to one-third of old growth if needed.
Care Details
Ideal Sunlight Coverage:
Full sun to partial shade (4–6 hours of direct sunlight daily); tolerates dappled light in hotter climates.
Sunlight Tolerance Tips:
Acclimate gradually to intense sunlight; protect from harsh afternoon sun; adjust placement based on seasonal light intensity.
Care Requirements
Care Difficulty
moderatemoderate
Sunlight
full sun to partial shade
Monitor leaf color for sun stress; use shade cloth if needed; rotate plant for even light exposure.
Watering
every 7–10 days during growing season, reduce in winter
Water thoroughly until runoff, allow soil to dry partially between waterings, and avoid waterlogging.
Soil
well-drained, loamy soil
pH: Slightly acidic to neutral (pH 6.0–7.0).
Test soil pH annually; amend as needed; avoid overwatering to prevent compaction.
Temperature
Hardy in USDA zones 4–8; tolerates temperatures between -30°F and 90°F; prefers cool winters for dormancy.
Protect from frost; ensure good air circulation; avoid placing near heat sources in winter.
Fertilizing
every 4–6 weeks during spring and summer
Fertilize sparingly; apply before new growth emerges; flush soil occasionally to prevent salt buildup.
Propagation
Methods
Softwood cuttings in late spring or early summer; seed propagation is possible but slower.
Step-by-Step Propagation Guide
- Take 4–6 inch cuttings.
- Remove lower leaves.
- Dip in rooting hormone.
- Plant in medium.
- Maintain humidity.
Best Time: Late spring to early summer when new growth is flexible but mature.
Environment
High humidity (70–90%), indirect light, and consistent warmth (65–75°F).
Medium
Well-draining mix of peat, perlite, and sand; rooting hormone is beneficial.
Hormone
Recommended for faster and more reliable rooting.
Timeline
Roots develop in 4–8 weeks; establishment may take an additional 1–2 months.
Tools Needed
Pruners, rooting hormone, misting spray bottle, plastic bags or propagation dome.
Quick Tips
Use clean tools; maintain consistent moisture; avoid direct sunlight during rooting.
Pruning & Repotting
Pruning Guide
Method
Thinning cuts to open the canopy; heading back to encourage branching.
Pruning Plan
Shape the plant to encourage bushier growth; remove dead or diseased wood; maintain air circulation.
Tools
Sharp bypass pruners, loppers for thicker branches, pruning saw for large stems.
Checklist
Sterilize tools; prune at the correct time; make clean cuts; dispose of pruned material.
Repotting Guide
Best Season
Early spring before active growth begins.
Pot Size
Increase pot size by 2–3 inches in diameter; avoid oversized pots.
Method
Remove plant gently; trim rootbound roots; replace with fresh soil mix; ensure good drainage.
Suggestions
Repot every 2–3 years or when roots fill the container; beneficial for younger plants to encourage growth.
Checklist
Check root health; use fresh soil; ensure drainage holes; water lightly after repotting.
Advanced Care Tips
Watering Mastery
Watering Checklist
Check soil moisture; water deeply; ensure drainage; avoid wetting foliage.
How to Apply Water Properly
Water directly at the root zone, ensuring even saturation to a depth of 6–8 inches. Water early in the morning to minimize evaporation and allow foliage to dry.
Watering Schedule Tips
Water deeply once per week during active growth, reducing frequency to every 2–3 weeks in winter. Adjust based on rainfall and soil moisture retention.
Soil Improvement
Add compost or aged manure; incorporate perlite or sand for drainage; use mulch to retain moisture.
Temperature Stress Management
Signs of Temperature Issues
Leaf scorch in excessive heat; leaf drop or dieback in prolonged cold; stunted growth in improper conditions.
Cold Stress
Leaves may wilt, discolor, or drop; branches can become brittle; root systems may suffer if soil freezes.
Solution: Mulch heavily around the base; protect with burlap in extreme cold; ensure well-drained soil to prevent frost heave.
Hot Stress
Wilting, leaf scorch, or premature leaf drop; reduced flowering; increased susceptibility to pests.
Solution: Provide afternoon shade; increase watering frequency; use reflective mulch to reduce soil temperature.
Fertilizing Guide
Fertilizing Checklist
Check fertilizer type; apply at recommended rates; water after fertilizing.
Fertilizing Method
Use balanced, slow-release fertilizer in early spring; avoid high-nitrogen formulas; discontinue in late summer to promote dormancy.
Common Problems & Solutions
Toxicity Warning
Cats
ToxicEuonymus atropurpureus is toxic to cats, with the seeds and berries posing the greatest risk. The toxic compounds can cause severe gastrointestinal upset and neurological symptoms in felines.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
if eaten
Dogs
ToxicThe seeds and berries of Euonymus atropurpureus are toxic to dogs, containing compounds that can disrupt gastrointestinal and neurological systems. Ingestion can lead to severe discomfort and potential systemic effects.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
if eaten
Humans
ToxicEuonymus atropurpureus contains toxic compounds, primarily alkaloids and glycosides, which can cause significant physiological distress upon ingestion. These compounds interfere with normal cellular functions, leading to gastrointestinal and neurological disturbances.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
if eaten
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is Euonymus atropurpureus toxic to pets?
A: Yes, it is mildly toxic to dogs and cats if ingested.
Q: Does this plant attract wildlife?
A: Yes, it attracts bees, butterflies, and birds due to its flowers and fruits.
Q: What are the common issues with this plant?
A: Common problems include leaf spots and wilting.
Quick Reference
| Family: | Celastraceae |
| Care: | moderate |
| Light: | full sun to partial shade |
| Water: | every 7–10 days during growi |
Get Expert Care Tips
Download the Plantious app for personalized care reminders and plant identification!
Google Play App Store