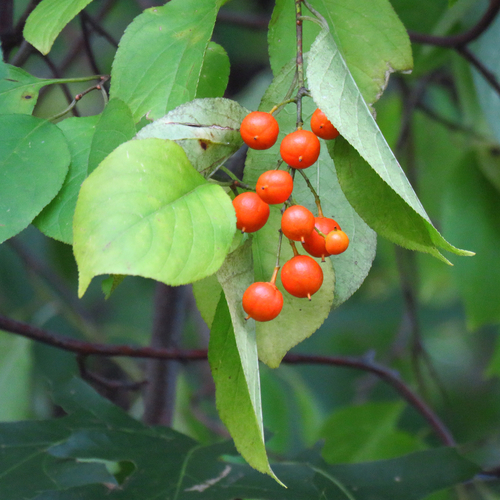
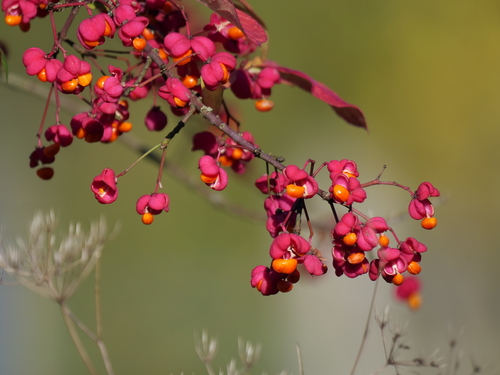Spindle Tree
euonymus latifolius
Also known as: ["Broad-leaved Spindle","European Spindle"]
Overview
A deciduous shrub native to Europe, known for its attractive foliage and bright pink fruits.
Benefits & Perks
["wildlife attractant (bees, butterflies, birds)","seasonal color change"]
Botanical Classification
| Phylum: | Magnoliophyta |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida |
| Order: | Celastrales |
| Family: | Celastraceae |
| Genus: | Euonymus |
| Botanical Name: | Euonymus latifolius |
Plant Characteristics
Basic Information
- Category: Shrubs
- Suitable Location: border plantings, woodland edges, or as a specimen shrub
- Suitable For:
- Is Weed: No
- Allergenicity: low
Environmental Needs
- Climate: {"temperatureRange":"–25–30°C"}
- Hardiness: {"zones":"3–7"}
- Misting: rarely required, only if ambient humidity is very low
- Drainage: Moderate drainage; avoid waterlogged conditions.
- Soil Type: Well-draining, loamy soil with added organic matter.
Maintenance Level
- Maintenance Level: moderate
- Toughness Level: moderate
- Pruning Frequency: Annually in late winter or early spring; light pruning can be done after flowering if needed.
- Pruning Intensity: Moderate pruning to shape and rejuvenate; avoid heavy pruning unless necessary for health.
Care Details
Ideal Sunlight Coverage:
Full sun to partial shade (4–6 hours of direct sunlight daily). Tolerates light shade but may become leggy with insufficient light.
Sunlight Tolerance Tips:
Acclimate plants gradually to intense sunlight to prevent scorching. In hot climates, provide afternoon shade. Indoors, place near a south or west-facing window with filtered light.
Care Requirements
Care Difficulty
easymoderate
Sunlight
full sun to partial shade
Rotate plant for even light exposure; use sheer curtains to filter intense sun; monitor for signs of sunburn.
Watering
every 7–10 days during growing season, reduce in winter
Water thoroughly but infrequently; ensure soil dries slightly between waterings; avoid waterlogging.
Soil
well-drained, loamy soil with moderate fertility
pH: Slightly acidic to neutral (pH 6.0–7.0).
Ensure good drainage; avoid compacted soil; mulch to retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Temperature
Hardy in USDA zones 4–7. Prefers cool to moderate temperatures (60–75°F or 15–24°C). Tolerates temperatures down to -20°F (-29°C) when established.
Protect from late spring frosts; water early to avoid heat stress; ensure good air circulation in warm weather.
Fertilizing
every 4–6 weeks during spring and summer
Test soil before fertilizing; apply fertilizer to moist soil; water after fertilizing to prevent root burn.
Propagation
Methods
Softwood cuttings taken in late spring or early summer.
Step-by-Step Propagation Guide
- Take 4–6 inch cuttings.
- Remove lower leaves.
- Dip in rooting hormone.
- Plant in medium.
- Maintain humidity.
- Transplant when rooted.
Best Time: Late spring to early summer when new growth is firm but not woody.
Environment
High humidity (70–80%), warm temperatures (70–75°F or 21–24°C), and bright indirect light.
Medium
Peat-based mix with added perlite or sand for drainage.
Hormone
Rooting hormone is recommended to improve success rates.
Timeline
Roots develop in 4–8 weeks; establish in new pots after 3–6 months.
Tools Needed
Pruning shears, rooting hormone, small pots, misting bottle, plastic bags or propagation dome.
Quick Tips
Use clean tools to prevent disease; maintain consistent moisture; provide bottom heat if possible.
Pruning & Repotting
Pruning Guide
Method
Use clean, sharp tools; make cuts just above a bud or lateral branch; remove crossing or crowded branches.
Pruning Plan
Prune to maintain shape, remove dead or diseased wood, and encourage bushier growth. Prune after flowering to avoid cutting off next year’s blooms.
Tools
Hand pruners, loppers, pruning saw, disinfectant (e.g., rubbing alcohol).
Checklist
Disinfect tools; prune at the right time; remove dead/diseased wood first; make clean cuts; avoid over-pruning.
Repotting Guide
Best Season
Early spring before new growth begins.
Pot Size
Increase pot size by 2–3 inches in diameter.
Method
Remove plant gently; trim any circling roots; place in a slightly larger pot with fresh, well-draining soil; water thoroughly.
Suggestions
Repot every 2–3 years or when roots fill the container. Euonymus latifolius is generally hardy and may not require frequent repotting if grown in-ground.
Checklist
Choose appropriate pot size; prepare fresh soil mix; handle roots carefully; water after repotting; place in appropriate light.
Advanced Care Tips
Watering Mastery
Watering Checklist
Check soil moisture before watering; water deeply; ensure drainage; avoid wetting leaves.
How to Apply Water Properly
Water at the base of the plant, ensuring moisture reaches the root zone. Water early in the morning to minimize evaporation and allow foliage to dry. Ensure excess water drains away to prevent root rot.
Watering Schedule Tips
Water deeply once per week during spring and summer, reducing frequency to every 2–3 weeks in fall and winter. Adjust based on rainfall and soil moisture.
Soil Improvement
Add compost or well-rotted manure to enhance fertility and structure; incorporate perlite or sand for better drainage.
Temperature Stress Management
Signs of Temperature Issues
Chlorosis or leaf drop in excessive heat; dieback or delayed growth in prolonged cold.
Cold Stress
Leaves may curl or turn brown at temperatures below -20°F (-29°C), especially if not acclimated or protected.
Solution: Mulch heavily around the base in fall; protect with burlap screens in extreme cold; avoid planting in exposed, windy sites.
Hot Stress
Wilting, leaf scorch, or reduced flowering during prolonged heat waves above 85°F (29°C).
Solution: Provide afternoon shade; increase watering frequency; use mulch to retain soil moisture; avoid fertilizing during heat stress.
Fertilizing Guide
Fertilizing Checklist
Check soil pH; use appropriate fertilizer; apply at recommended rate; water after application.
Fertilizing Method
Use a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in early spring. Apply a light dose of liquid fertilizer monthly during growing season (April–August). Avoid fertilizing in fall and winter.
Common Problems & Solutions
Toxicity Warning
Cats
Slightly ToxicCats may experience mild gastrointestinal irritation if they consume parts of Euonymus latifolius, particularly the berries and seeds. The alkaloids present can cause discomfort but are not typically life-threatening.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
if eaten
Dogs
Slightly ToxicIn dogs, ingestion of Euonymus latifolius berries or seeds can lead to mild gastrointestinal upset due to the presence of alkaloids. Symptoms are generally not severe but can cause discomfort.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
if eaten
Humans
Slightly ToxicEuonymus latifolius contains alkaloids and other compounds that can cause mild gastrointestinal distress and irritation upon ingestion. The berries and seeds are the most toxic parts, containing higher concentrations of these compounds.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
if eaten
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is Euonymus latifolius toxic to pets?
A: Yes, it is mildly toxic to dogs and cats if ingested.
Q: Does Euonymus latifolius attract wildlife?
A: Yes, it attracts bees, butterflies, and birds due to its flowers and fruits.
Q: How should Euonymus latifolius be pruned?
A: Prune in late winter or early spring to maintain shape and remove dead or diseased branches.
Quick Reference
| Family: | Celastraceae |
| Care: | easy |
| Light: | full sun to partial shade |
| Water: | every 7–10 days during growi |
Get Expert Care Tips
Download the Plantious app for personalized care reminders and plant identification!
Google Play App Store