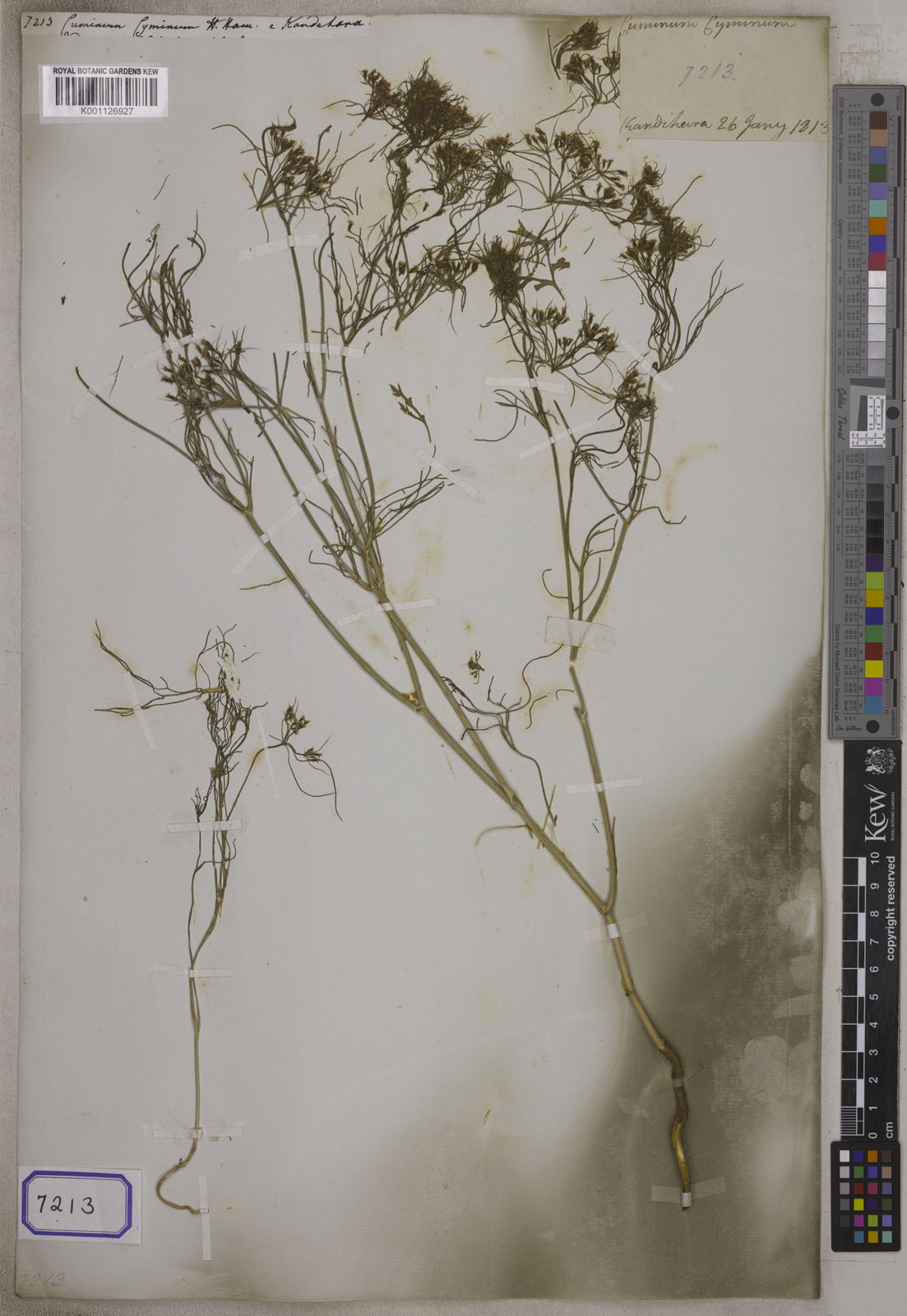
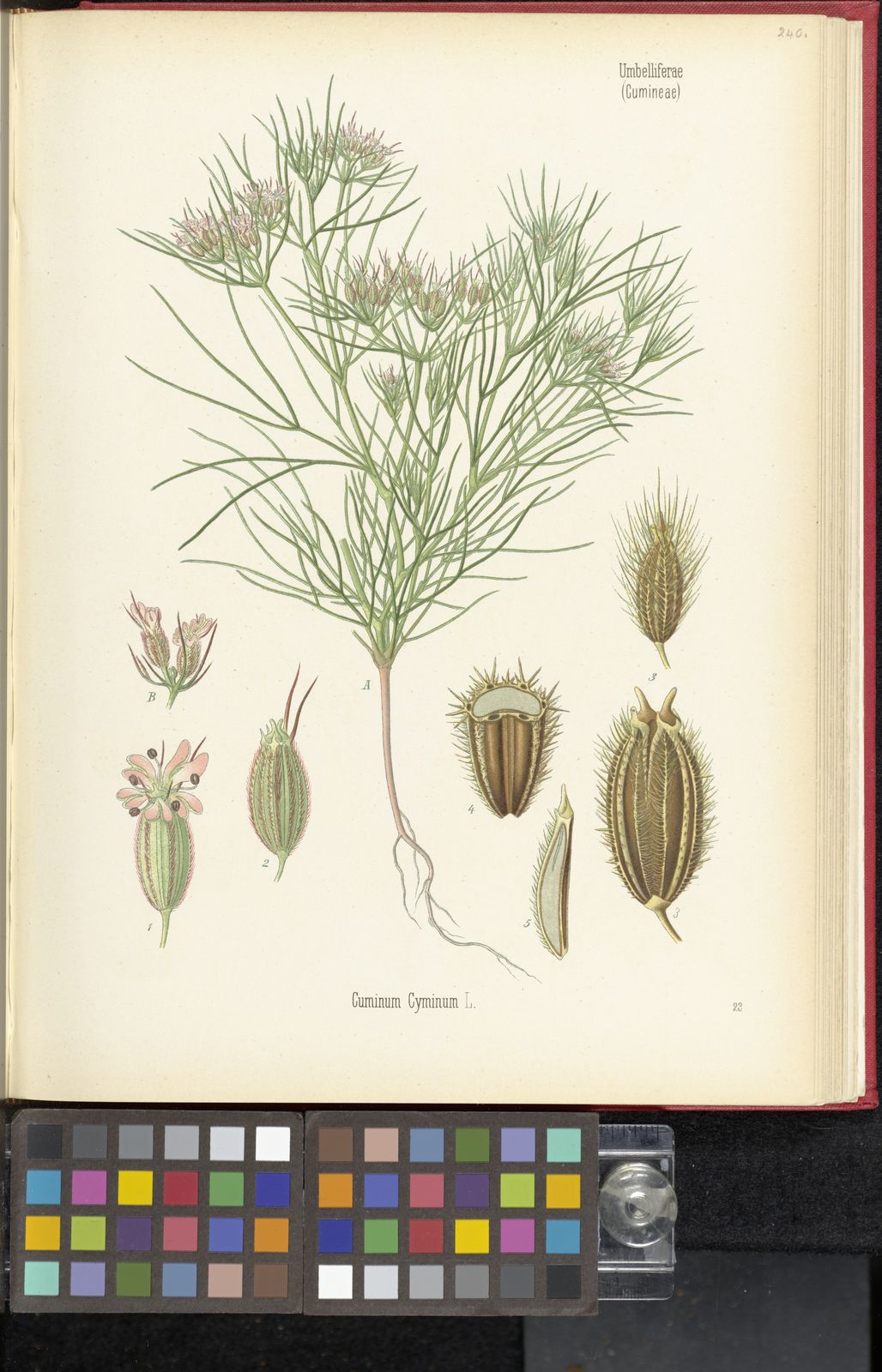
Cumin
cuminum cyminum
Also known as: ["comino","jeera"]
Overview
An annual herbaceous plant in the Apiaceae family, cultivated for its aromatic seeds used as a spice.
Benefits & Perks
["culinary herb","fragrant flowers","medicinal use"]
Botanical Classification
| Phylum: | Magnoliophyta |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida |
| Order: | Apiales |
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Genus: | Cuminum |
| Botanical Name: | Cuminum cyminum |
Plant Characteristics
Basic Information
- Category: Herbs & Weeds
- Suitable Location: outdoor garden bed in full sun, or container with excellent drainage
- Suitable For:
- Is Weed: No
- Allergenicity: low
Environmental Needs
- Climate: {"temperatureRange":"15–30°C"}
- Hardiness: {"zones":"8–11"}
- Misting: rarely required, only if ambient humidity is very low
- Drainage: Fast-draining.
- Soil Type: Well-draining, sandy loam with some organic matter.
Maintenance Level
- Maintenance Level: moderate
- Toughness Level: moderate
- Pruning Frequency: As needed; lightly prune after flowering or when plants become leggy.
- Pruning Intensity: Light to moderate.
Care Details
Ideal Sunlight Coverage:
Full sun (6–8 hours of direct sunlight per day); adjust for extreme heat by providing partial shade.
Sunlight Tolerance Tips:
Acclimate seedlings gradually to direct sun; protect from intense midday sun in hot climates; ensure proper ventilation if grown indoors.
Care Requirements
Care Difficulty
easyeasy
Sunlight
full sun
Rotate plants for even growth; use shade cloth in extreme heat; avoid placing near reflective surfaces.
Watering
every 7–10 days during active growth, reduce in winter
Avoid overwatering; water deeply but infrequently; ensure good drainage.
Soil
well-draining, sandy loam with moderate fertility
pH: Slightly alkaline (pH 7.0–8.0).
Ensure soil dries between waterings; avoid heavy clay soils; amend with organic matter.
Temperature
Warm temperatures (20–30°C); tolerates mild frost but thrives in heat.
Avoid sudden temperature changes; protect from frost; ensure good air circulation.
Fertilizing
every 4–6 weeks during growing season
Fertilize sparingly; avoid high-nitrogen formulas; stop in winter.
Propagation
Methods
Seeds or stem cuttings.
Step-by-Step Propagation Guide
- Sow seeds 1/4 inch deep or take 4–6 inch cuttings, remove lower leaves, and plant in moist medium.
Best Time: Spring or early summer when temperatures are warm.
Environment
Warm, humid conditions with bright indirect light.
Medium
Well-draining soil mix with sand or perlite.
Hormone
Not necessary for seeds; optional for stem cuttings.
Timeline
Seeds germinate in 7–14 days; cuttings root in 2–4 weeks.
Tools Needed
Seed trays, pruners, rooting hormone (optional), misting bottle.
Quick Tips
Keep soil consistently moist; provide warmth; use bottom heat for faster germination.
Pruning & Repotting
Pruning Guide
Method
Pinch back stems to encourage bushier growth; remove yellow or dead leaves.
Pruning Plan
Minimal pruning; focus on removing dead or damaged foliage to encourage airflow.
Tools
Pruning shears, gloves.
Checklist
Sterilize tools; prune dead growth; avoid over-pruning.
Repotting Guide
Best Season
Spring, before the active growing season.
Pot Size
One size up from current pot; ensure good drainage holes.
Method
Gently remove the plant, trim any circling roots, and repot in fresh, well-draining soil.
Suggestions
Repot only if the plant becomes root-bound; typically not necessary for annual cultivation.
Checklist
Use fresh soil; check for root rot; ensure proper drainage.
Advanced Care Tips
Watering Mastery
Watering Checklist
Check soil moisture before watering; water early morning; ensure drainage; reduce in winter.
How to Apply Water Properly
Water at the base of the plant, ensuring moisture reaches the root zone without saturating the soil. Water early in the morning to minimize evaporation.
Watering Schedule Tips
Water lightly and infrequently, allowing the soil to dry out between waterings. Reduce watering during winter dormancy.
Soil Improvement
Add sand or perlite to improve drainage; incorporate compost for fertility.
Temperature Stress Management
Signs of Temperature Issues
Wilting, yellowing leaves, stunted growth, or flower drop.
Cold Stress
Slows growth, may cause leaf drop, and can lead to fungal infections in damp conditions.
Solution: Move to a warmer location; cover with a frost cloth if outdoors; reduce watering.
Hot Stress
Leaf scorch, wilting, and reduced flowering due to excessive heat.
Solution: Provide partial shade during peak heat; increase watering; use mulch to retain soil moisture.
Fertilizing Guide
Fertilizing Checklist
Use diluted fertilizer; apply during growing season; avoid winter feeding.
Fertilizing Method
Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer diluted to half strength every 4–6 weeks during the growing season; avoid fertilizing in winter.
Common Problems & Solutions
Toxicity Warning
Cats
Non-toxicCuminum cyminum is not considered toxic to cats when consumed in small quantities. However, large amounts may cause mild gastrointestinal upset.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Dogs
Non-toxicCuminum cyminum is not considered toxic to dogs when consumed in small quantities. However, large amounts may cause mild gastrointestinal upset.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Humans
Non-toxicCuminum cyminum, commonly known as cumin, is widely used as a culinary spice and is generally considered non-toxic for human consumption. It has been used for centuries in traditional medicine and cooking without significant adverse effects.
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is cumin safe for pets?
A: Yes, cumin is non-toxic to dogs and cats in culinary amounts.
Q: How do I grow cumin?
A: Sow seeds in well-drained soil in full sun after the last frost.
Q: What are the uses of cumin?
A: Cumin is used as a spice in cooking and has traditional medicinal applications.
Quick Reference
| Family: | Apiaceae |
| Care: | easy |
| Light: | full sun |
| Water: | every 7–10 days during activ |
Get Expert Care Tips
Download the Plantious app for personalized care reminders and plant identification!
Google Play App Store