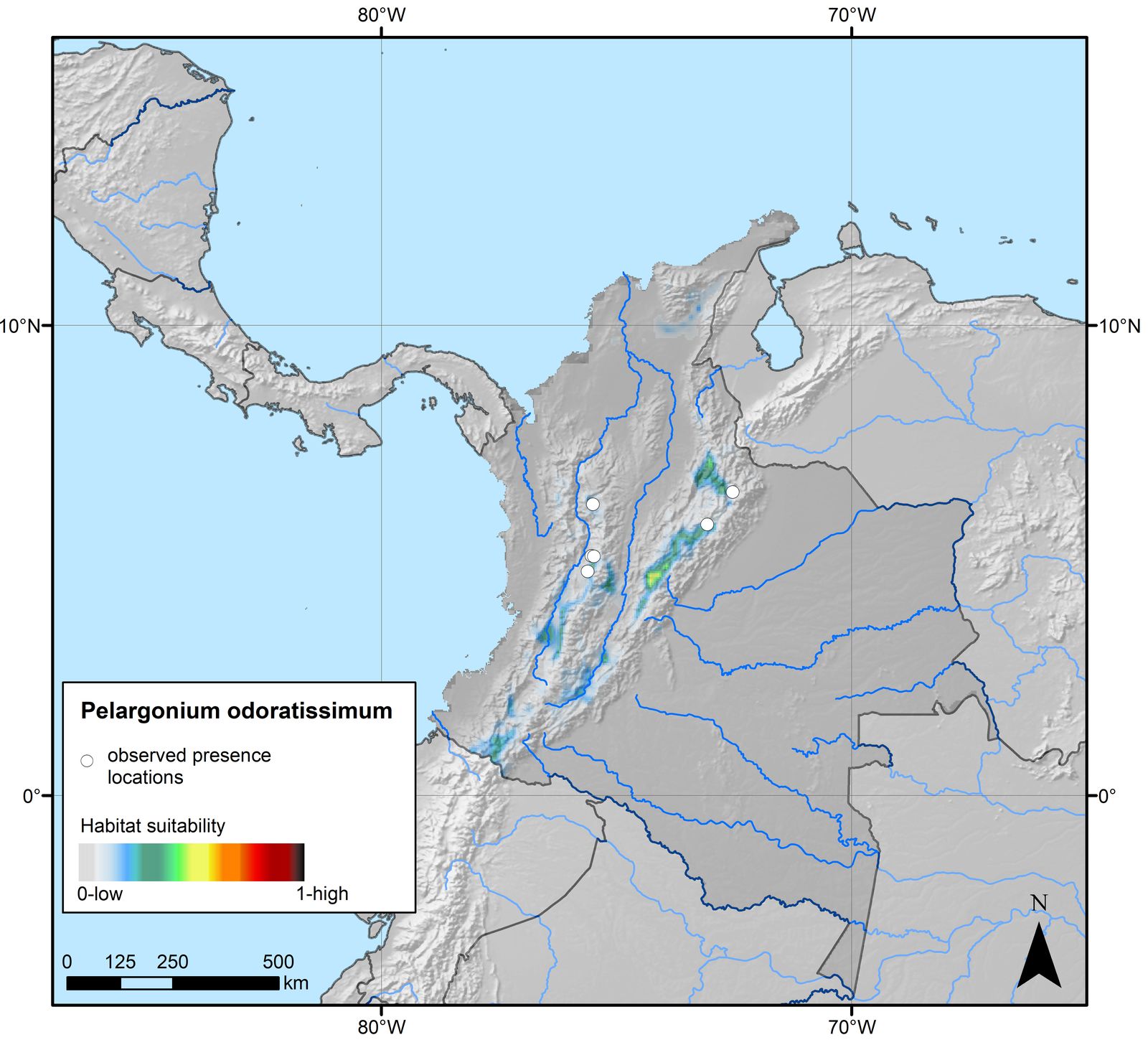
Apple Geranium
pelargonium odoratissimum
Also known as: ["Fragrant Geranium","Apple Scented Geranium"]
Overview
A perennial subshrub with fragrant, apple-scented leaves and small pinkish-white flowers.
Benefits & Perks
["fragrant flowers","aesthetic foliage","low maintenance"]
Botanical Classification
| Phylum: | Magnoliophyta |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida |
| Order: | Geraniales |
| Family: | Geraniaceae |
| Genus: | Pelargonium |
| Botanical Name: | Pelargonium odoratissimum |
Plant Characteristics
Basic Information
- Category: Leaf Plants
- Suitable Location: indoor pot near bright window or outdoor garden bed in mild climates
- Suitable For:
- Is Weed: No
- Allergenicity: low
Environmental Needs
- Climate: {"temperatureRange":"5–30°C"}
- Hardiness: {"zones":"9–11"}
- Misting: rarely required, only if ambient humidity is very low
- Drainage: Fast-draining
- Soil Type: Well-draining potting mix with added perlite or sand
Maintenance Level
- Maintenance Level: low
- Toughness Level: moderate
- Pruning Frequency: Annually in late winter or early spring; light pruning can be done as needed.
- Pruning Intensity: Moderate; remove up to one-third of the plant if overgrown.
Care Details
Ideal Sunlight Coverage:
Bright indirect light for 6–8 hours daily; can tolerate some direct morning sun but avoid harsh afternoon sun.
Sunlight Tolerance Tips:
Acclimate gradually to direct sun; protect from intense midday sun; place in a spot with filtered light if outdoors.
Care Requirements
Care Difficulty
easyeasy
Sunlight
full sun to partial shade
Rotate plant weekly for even growth; use sheer curtains to filter intense light; avoid direct afternoon sun.
Watering
every 7–10 days during active growth, reduce in winter
Allow soil to dry between waterings; avoid overwatering; water early in the day.
Soil
well-draining, sandy loam with some organic matter
pH: Slightly acidic to neutral (6.0–7.0)
Ensure pots have drainage holes; avoid heavy garden soil; top-dress with compost annually.
Temperature
Prefers 60–75°F (15–24°C); can tolerate mild frosts but thrives in moderate temperatures.
Avoid sudden temperature changes; protect from cold drafts; ensure good air circulation.
Fertilizing
every 4–6 weeks during spring and summer
Fertilize less in winter; apply to moist soil to prevent root burn; flush soil occasionally to prevent salt buildup.
Propagation
Methods
Stem cuttings
Step-by-Step Propagation Guide
- Take a 4–6 inch cutting.
- Remove lower leaves.
- Dip in rooting hormone (optional).
- Plant in moist medium.
- Keep humid and warm.
Best Time: Spring or early summer when the plant is actively growing.
Environment
Warm (70–75°F), high humidity, indirect light
Medium
Well-draining mix of peat and perlite or cactus mix
Hormone
Optional but recommended for faster rooting
Timeline
Roots in 2–4 weeks; establish in 2–3 months
Tools Needed
Pruners, rooting hormone, small pots, misting spray bottle
Quick Tips
Use healthy, non-flowering stems; keep soil consistently moist but not waterlogged; provide bottom heat if possible.
Pruning & Repotting
Pruning Guide
Method
Cut stems just above a leaf node; remove crossing or crowded branches.
Pruning Plan
Shape the plant; encourage bushier growth; remove dead or overgrown stems.
Tools
Clean, sharp pruners or scissors
Checklist
Sterilize tools; prune during dormancy; remove dead/damaged growth; shape evenly.
Repotting Guide
Best Season
Spring, before the active growing season begins.
Pot Size
One size up (e.g., from 4-inch to 6-inch pot); ensure good drainage.
Method
Remove plant gently; trim roots if needed; place in a slightly larger pot with fresh soil; water lightly.
Suggestions
Repot every 2–3 years or when roots fill the pot; beneficial for growth and soil freshness.
Checklist
Check root bound status; prepare new pot with drainage; use fresh soil mix; water sparingly after repotting.
Advanced Care Tips
Watering Mastery
Watering Checklist
Check soil moisture; water deeply; ensure drainage; adjust for season.
How to Apply Water Properly
Water deeply at the root zone until water drains from the bottom; ensure excess water drains away to prevent waterlogging; water in the morning to allow foliage to dry.
Watering Schedule Tips
Water thoroughly when the top inch of soil feels dry; reduce frequency in winter to prevent root rot.
Soil Improvement
Add perlite or coarse sand for drainage; incorporate organic matter like compost for fertility.
Temperature Stress Management
Signs of Temperature Issues
Yellowing leaves (cold stress); wilting or leaf drop (heat stress).
Cold Stress
Slows growth; may cause leaf discoloration; vulnerable to frost damage below 28°F (-2°C).
Solution: Move to a warmer location; protect from drafts; cover if frost is expected.
Hot Stress
Leaves may wilt, scorch, or drop; growth may slow under prolonged heat.
Solution: Provide shade during peak heat; increase humidity; water more frequently but avoid waterlogging.
Fertilizing Guide
Fertilizing Checklist
Check season; dilute fertilizer; apply to moist soil; avoid winter feeding.
Fertilizing Method
Use a balanced liquid fertilizer diluted to half strength every 4–6 weeks during growing season (spring/summer); avoid fertilizing in winter.
Common Problems & Solutions
Toxicity Warning
Cats
Non-toxicPelargonium odoratissimum is not known to be toxic to cats. Its mild scent and properties make it a safe plant for feline environments.
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Dogs
Non-toxicPelargonium odoratissimum is not known to be toxic to dogs. It is often used in pet-friendly environments for its pleasant fragrance.
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Humans
Non-toxicPelargonium odoratissimum is generally considered non-toxic to humans. It is commonly used in aromatherapy and as a culinary herb due to its apple-like scent and flavor.
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How do I propagate Pelargonium odoratissimum?
A: It can be propagated by stem cuttings in spring or summer.
Q: What are the ideal growing conditions for this plant?
A: It thrives in full sun to partial shade with well-draining soil and moderate watering.
Q: Can the leaves be used for culinary purposes?
A: Yes, the leaves have an apple-like scent and can be used in teas or potpourri.
Quick Reference
| Family: | Geraniaceae |
| Care: | easy |
| Light: | full sun to partial shade |
| Water: | every 7–10 days during activ |
Get Expert Care Tips
Download the Plantious app for personalized care reminders and plant identification!
Google Play App Store