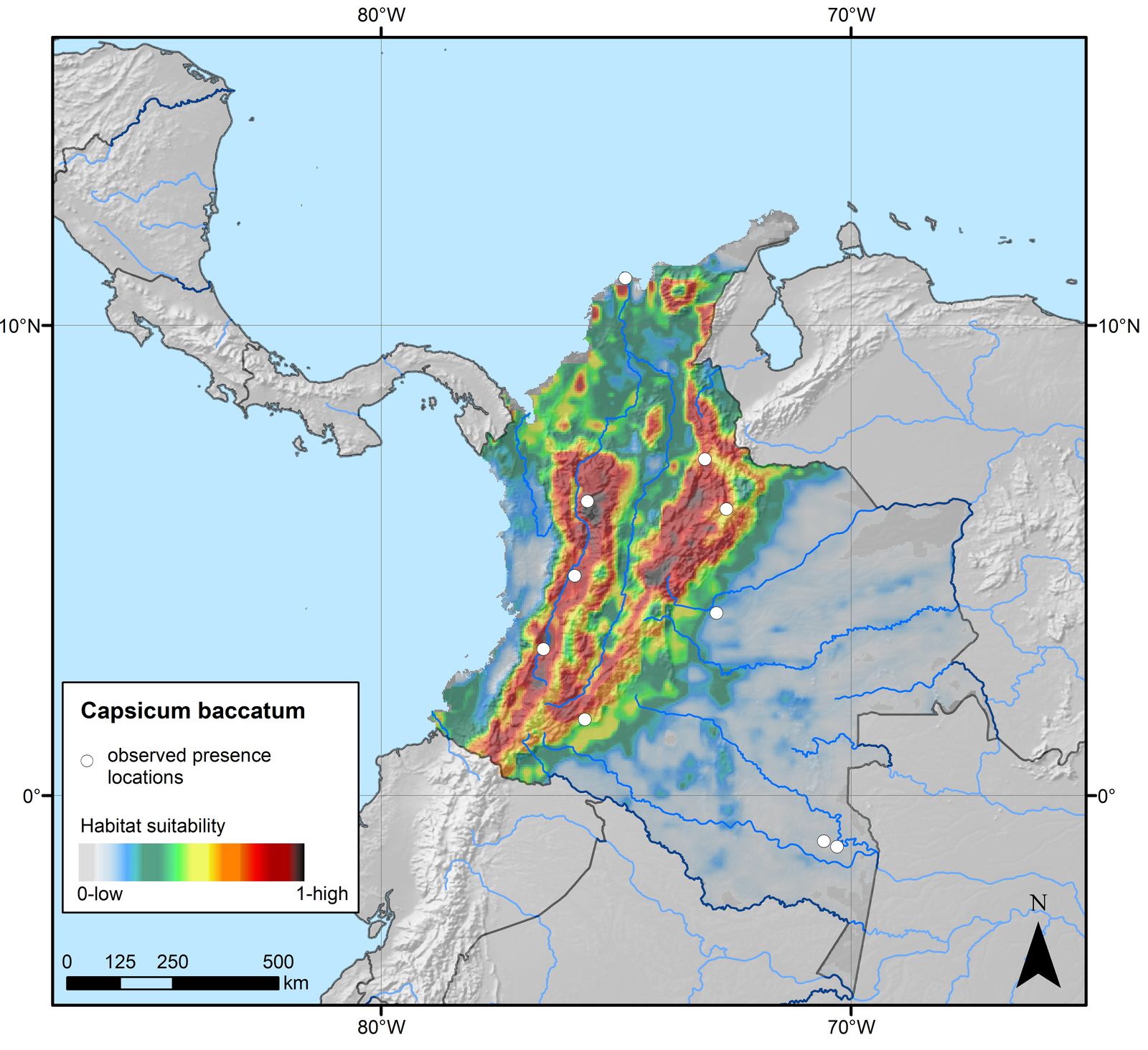
Aji Pepper
capsicum baccatum
Also known as: ["Aji","Lemon Drop","Aji Amarillo"]
Overview
A species of chili pepper native to South America, known for its vibrant colors and fruity flavor profile.
Benefits & Perks
["edible fruits","culinary herb","aesthetic foliage"]
Botanical Classification
| Phylum: | Magnoliophyta |
| Class: | Magnoliopsida |
| Order: | Solanales |
| Family: | Solanaceae |
| Genus: | Capsicum |
| Botanical Name: | Capsicum baccatum |
Plant Characteristics
Basic Information
- Category: Fruits
- Suitable Location: outdoor garden bed in full sun or container with at least 6 hours of direct sunlight
- Suitable For:
- Is Weed: No
- Allergenicity: low
Environmental Needs
- Climate: {"temperatureRange":"18–32°C"}
- Hardiness: {"zones":"9–11"}
- Misting: rarely required, only if grown in very dry indoor conditions
- Drainage: Fast-draining to prevent waterlogging.
- Soil Type: Well-draining, loamy soil with added organic matter; cactus or succulent mix can be used.
Maintenance Level
- Maintenance Level: moderate
- Toughness Level: moderate
- Pruning Frequency: Light pruning every 4–6 weeks during growing season; major pruning in late winter or early spring.
- Pruning Intensity: Moderate; remove up to one-third of growth at a time to avoid shock.
Care Details
Ideal Sunlight Coverage:
Full sun (6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily); adjust for extreme heat by providing partial shade during peak afternoon hours.
Sunlight Tolerance Tips:
Gradually acclimate plants to full sun to avoid scorching; provide shade during extreme heat; ensure proper ventilation if grown indoors.
Care Requirements
Care Difficulty
moderatemoderate
Sunlight
full sun
Rotate plants for even light exposure; use reflective surfaces to enhance light; monitor for signs of sunburn.
Watering
every 7–10 days, allowing soil to dry slightly between waterings
Water thoroughly until it drains from the bottom, avoid wetting foliage, and ensure proper drainage to prevent waterlogging.
Soil
well-draining, loamy soil with added organic matter
pH: Slightly acidic to neutral (6.0–7.0).
Ensure pots have drainage holes, avoid compacted soil, test pH periodically, amend as needed.
Temperature
Optimal range 70–85°F (21–29°C); prefers warm, stable temperatures; reduce watering in cooler temperatures.
Use shade cloth in extreme heat; protect from frost; maintain consistent temperatures for optimal growth.
Fertilizing
every 4–6 weeks during growing season with balanced liquid fertilizer
Avoid over-fertilizing to prevent salt buildup; water before fertilizing to prevent root burn; use a fertilizer with higher phosphorus for fruit development.
Propagation
Methods
Stem cuttings or seeds; stem cuttings are faster and more reliable for home growers.
Step-by-Step Propagation Guide
- Take a 4–6 inch cutting, remove lower leaves, apply rooting hormone, plant in medium, keep moist and warm, transplant once rooted.
Best Time: Spring or early summer when temperatures are warm and growth is active.
Environment
Warm (70–80°F), high humidity (70–80%), and indirect light.
Medium
Well-draining mix of perlite and peat moss or cactus mix.
Hormone
Recommended to use rooting hormone for faster and more reliable rooting.
Timeline
Roots typically form in 2–4 weeks; plants may take 2–3 months to establish.
Tools Needed
Pruning shears, rooting hormone, small pots, well-draining medium, misting bottle.
Quick Tips
Use sterile tools to prevent disease; keep cuttings out of direct sun; maintain consistent moisture.
Pruning & Repotting
Pruning Guide
Method
Pinch back tips for bushier growth, cut back leggy stems, remove dead or yellowing leaves.
Pruning Plan
Prune to improve air circulation, encourage bushier growth, and remove diseased or non-productive branches.
Tools
Pruning shears, sterilizing solution, gloves.
Checklist
Sterilize tools, prune during dry weather, remove dead/diseased parts, make clean cuts, clean up debris.
Repotting Guide
Best Season
Spring, before the active growing season begins.
Pot Size
Increase pot size by 2–3 inches in diameter; ensure good drainage holes.
Method
Gently remove plant, trim roots if necessary, place in a new pot with fresh soil, water thoroughly, and allow to drain.
Suggestions
Repot every 1–2 years or when roots outgrow the pot; beneficial for nutrient replenishment and root health.
Checklist
Choose appropriate pot, prepare fresh soil mix, trim roots if needed, water after repotting, place in appropriate light.
Advanced Care Tips
Watering Mastery
Watering Checklist
Check soil moisture, water deeply, ensure drainage, avoid wetting leaves, adjust for season.
How to Apply Water Properly
Water directly at the base of the plant, ensuring the root zone is saturated but not waterlogged; allow excess water to drain away to prevent root rot.
Watering Schedule Tips
Water deeply once the top inch of soil feels dry; reduce frequency in winter to prevent root rot.
Soil Improvement
Add perlite or sand for drainage, incorporate compost for fertility, use mulch to retain moisture.
Temperature Stress Management
Signs of Temperature Issues
Chlorosis, wilting, bud drop, stunted growth, or leaf burn.
Cold Stress
Low temperatures slow growth, cause leaf discoloration, and increase susceptibility to diseases.
Solution: Provide frost protection, move plants indoors, use row covers, or place heat sources nearby.
Hot Stress
Excessive heat can lead to wilting, flower drop, and reduced fruit set.
Solution: Provide shade during peak heat, increase watering, use mulch to retain moisture, and ensure good air circulation.
Fertilizing Guide
Fertilizing Checklist
Check fertilizer type, dilute according to instructions, apply to moist soil, avoid contact with foliage, flush periodically to prevent salt buildup.
Fertilizing Method
Use a balanced, water-soluble fertilizer every 4–6 weeks during growing season; reduce or stop in winter.
Common Problems & Solutions
Toxicity Warning
Cats
Slightly ToxicCapsicum baccatum is slightly toxic to cats, primarily due to its capsaicin content, which can irritate the gastrointestinal tract. The effects are generally mild and localized, with no severe systemic toxicity.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
if eaten
Dogs
Slightly ToxicCapsicum baccatum can be slightly toxic to dogs due to its capsaicin content, which may cause mild gastrointestinal irritation. The physiological impact is limited to the digestive tract, with no significant systemic effects.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
if eaten
Humans
Non-toxicCapsicum baccatum, commonly known as Aji pepper, is generally considered non-toxic to humans. However, excessive consumption may cause gastrointestinal discomfort due to its capsaicin content. The physiological impact is primarily localized to the digestive system, with no systemic toxicity.
⚠️ Symptoms:
🌿 Toxic Parts:
⚡ Toxic If:
if eaten in excessive quantities
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is Capsicum baccatum edible?
A: Yes, its fruits are edible and widely used in culinary applications.
Q: How should I care for Capsicum baccatum?
A: Provide full sun, well-drained soil, and regular watering for optimal growth.
Q: Are the peppers of Capsicum baccatum hot?
A: Yes, they have a moderate to high heat level, depending on the variety.
Quick Reference
| Family: | Solanaceae |
| Care: | moderate |
| Light: | full sun |
| Water: | every 7–10 days, allowing so |
Get Expert Care Tips
Download the Plantious app for personalized care reminders and plant identification!
Google Play App Store