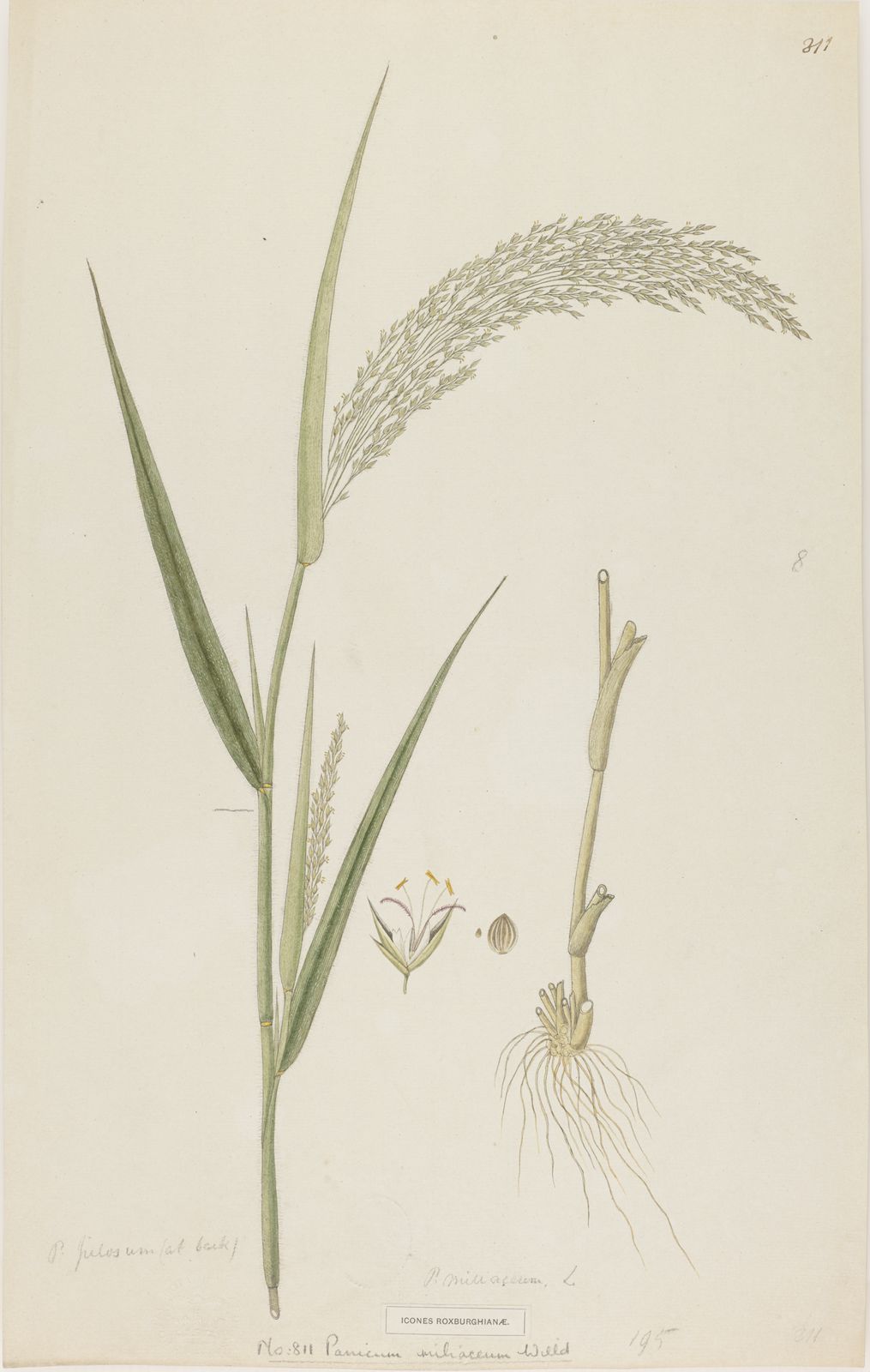
Broomcorn millet
panicum miliaceum
Also known as: ["Broom corn millet","Common millet","Yellow millet"]
Overview
An annual grass cultivated for its grain, which is used as a staple food in many parts of the world.
Benefits & Perks
["edible fruits","fast growing","drought tolerant"]
Botanical Classification
| Phylum: | Magnoliophyta |
| Class: | Liliopsida |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Panicum |
| Botanical Name: | Panicum miliaceum |
Plant Characteristics
Basic Information
- Category: Grains
- Suitable Location: outdoor garden in open field
- Suitable For:
- Is Weed: No
- Allergenicity: low
Environmental Needs
- Climate: {"temperatureRange":"10–35°C"}
- Hardiness: {"zones":"4–9"}
- Misting: rarely required
- Drainage: Well-draining to moderately draining.
- Soil Type: Loamy, fertile soil with good organic matter.
Maintenance Level
- Maintenance Level: low
- Toughness Level: high
- Pruning Frequency: As needed; typically after harvest or if plants become overcrowded.
- Pruning Intensity: Light; focus on tidiness rather than shaping.
Care Details
Ideal Sunlight Coverage:
Full sun (6–8 hours/day); tolerates partial shade but may produce fewer grains.
Sunlight Tolerance Tips:
Acclimate gradually if moving from shade to sun; avoid sudden exposure to intense midday sun to prevent scorching; outdoor placement is ideal for maximum yield.
Care Requirements
Care Difficulty
easyeasy
Sunlight
full sun
Rotate plants for even light, use shade cloth in extreme heat, maximize sun exposure during growing season.
Watering
every 7–10 days during active growth, reduce in winter
Water evenly, avoid waterlogging, and ensure good drainage.
Soil
well-drained, fertile loam
pH: 6.0–7.5 (slightly acidic to neutral).
Test soil pH, amend with organic matter, ensure good drainage.
Temperature
Warm-season crop; ideal 70–85°F (21–29°C); thrives in hot summers.
Use frost protection in early growth, monitor soil temperature, adjust watering in heat.
Fertilizing
every 4–6 weeks during growing season
Apply fertilizer before heavy rain, avoid contact with roots, reduce feeding in late summer.
Propagation
Methods
Seed propagation; direct sow or start indoors 4–6 weeks before last frost.
Step-by-Step Propagation Guide
- Prepare soil, sow seeds 1/4–1/2 inch deep, thin seedlings, water gently.
Best Time: Spring, after soil warms to 65°F (18°C).
Environment
Warm soil, full sun, consistent moisture until established.
Medium
Well-draining soil mix; can be sown directly in garden beds.
Hormone
Not required for seeds.
Timeline
Germination in 7–14 days; mature plant in 60–90 days.
Tools Needed
Garden trowel, watering can, seed tray (if starting indoors).
Quick Tips
Sow thickly for better germination, thin seedlings to 6–8 inches apart, keep soil consistently moist.
Pruning & Repotting
Pruning Guide
Method
Snip stems at the base with clean cuts.
Pruning Plan
Minimal pruning needed; remove dead or damaged stems if necessary.
Tools
Hand pruners, scissors.
Checklist
Check for dead stems, use clean tools, dispose of debris.
Repotting Guide
Best Season
N/A
Pot Size
N/A
Method
N/A
Suggestions
Not typically repotted; grows as an annual in garden beds.
Checklist
N/A
Advanced Care Tips
Watering Mastery
Watering Checklist
Check soil moisture, water deeply, ensure drainage, adjust for season.
How to Apply Water Properly
Water at the base of the plant, ensuring moisture reaches the root zone without wetting foliage; allow excess water to drain away.
Watering Schedule Tips
Water deeply once the top inch of soil is dry; reduce frequency in winter to prevent root rot.
Soil Improvement
Add compost or aged manure before planting; incorporate sand if soil is heavy clay.
Temperature Stress Management
Signs of Temperature Issues
Chlorosis or wilting in extreme heat; stunted growth or poor germination in cold.
Cold Stress
Seeds may fail to germinate; young plants can suffer frost damage or die.
Solution: Start seeds indoors or use row covers in early spring; avoid planting in cold soil.
Hot Stress
Wilting, leaf scorch, or reduced grain yield in prolonged extreme heat.
Solution: Provide partial shade during peak heat, maintain consistent soil moisture, and ensure good air circulation.
Fertilizing Guide
Fertilizing Checklist
Check soil fertility, apply at planting, side-dress during growth, stop before flowering.
Fertilizing Method
Use balanced fertilizer (10-10-10) at planting; side-dress with nitrogen during vegetative growth; avoid over-fertilizing to prevent lodging.
Common Problems & Solutions
Toxicity Warning
Cats
Non-toxicProso millet is not considered toxic to cats and can be included in their diet in moderation. However, it should not constitute a significant portion of their diet due to their specific nutritional requirements.
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Dogs
Non-toxicProso millet is not considered toxic to dogs and can be included in their diet in moderation. It is a source of carbohydrates and can be a part of a balanced diet for canines.
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Humans
Non-toxicPanicum miliaceum, commonly known as proso millet, is a cereal grain that is generally considered safe for human consumption. It is widely cultivated and used as a staple food in many parts of the world.
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is Broomcorn millet safe for human consumption?
A: Yes, it is a staple food in many regions and is non-toxic to humans.
Q: How does Broomcorn millet grow?
A: It is an annual grass that grows quickly and is drought-tolerant, making it suitable for arid regions.
Q: Can Broomcorn millet be grown in containers?
A: While possible, it is typically grown in fields due to its height and grain production needs.
Quick Reference
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Care: | easy |
| Light: | full sun |
| Water: | every 7–10 days during activ |
Get Expert Care Tips
Download the Plantious app for personalized care reminders and plant identification!
Google Play App Store