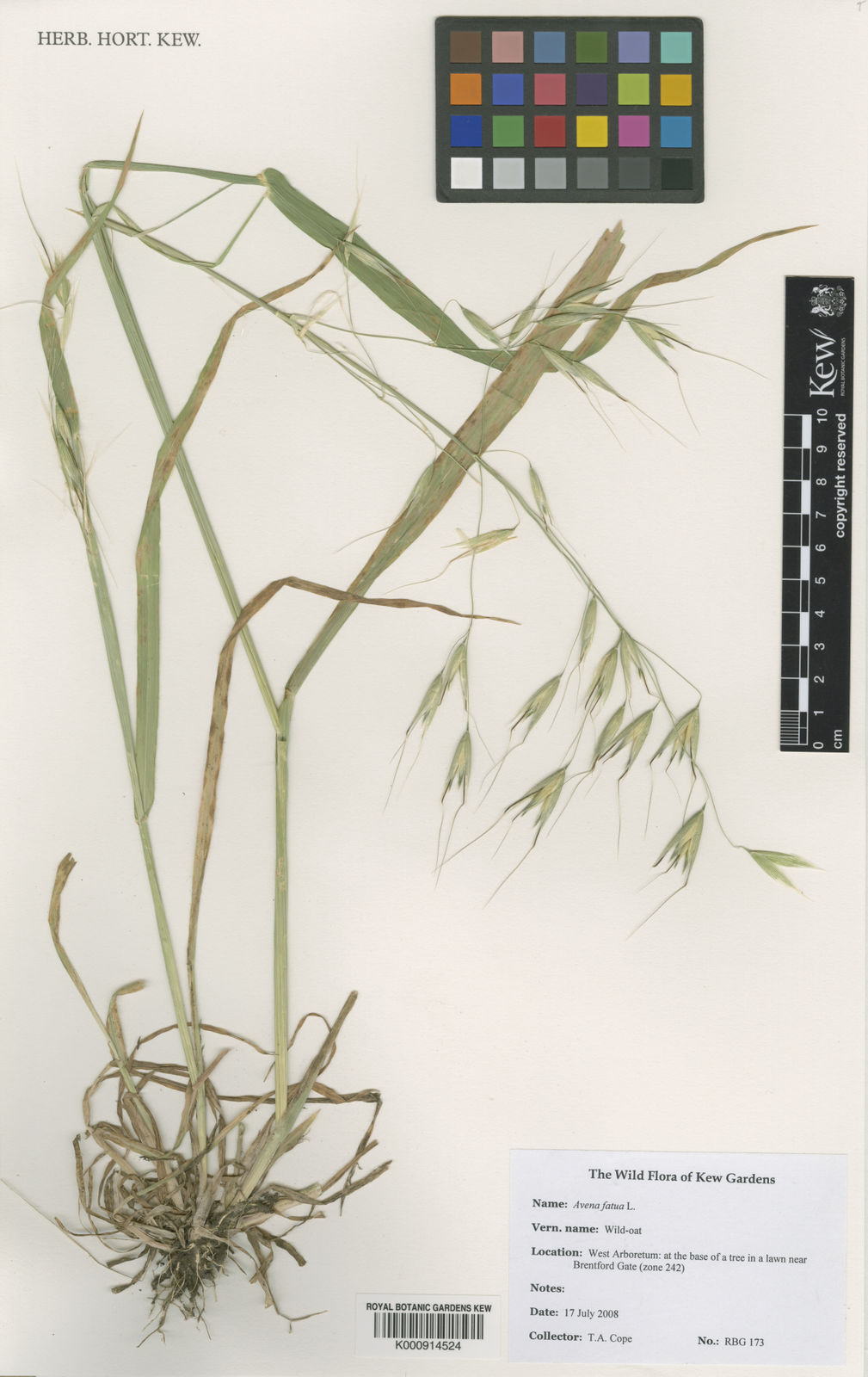
Wild Oat
avena fatua
Also known as: ["Wild Oats","Wild Oat Grass"]
Overview
A tall, annual grass species native to Europe and Asia, often considered a weed in agricultural settings due to its competitiveness with crops.
Benefits & Perks
["fast growing","wildlife attractant (bees, butterflies, birds)","drought tolerant"]
Botanical Classification
| Phylum: | Magnoliophyta |
| Class: | Liliopsida |
| Order: | Poales |
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Genus: | Avena |
| Botanical Name: | Avena fatua |
Plant Characteristics
Basic Information
- Category: Grasses
- Suitable Location: open fields, meadows, or disturbed areas
- Suitable For:
- Is Weed: No
- Allergenicity: low
Environmental Needs
- Climate: {"temperatureRange":"5–35°C"}
- Hardiness: {"zones":"3–9"}
- Misting: not required
- Drainage: Moderate to fast-draining.
- Soil Type: Adaptable to various soil types; prefers well-draining, loamy soil.
Maintenance Level
- Maintenance Level: very low
- Toughness Level: very high
- Pruning Frequency: As needed; typically minimal pruning for wild oats.
- Pruning Intensity: Light; only remove dead or diseased parts.
Care Details
Ideal Sunlight Coverage:
Full sun (6–8 hours of direct sunlight daily); tolerates partial shade but may produce fewer seeds.
Sunlight Tolerance Tips:
Acclimate seedlings gradually to direct sun; protect from intense midday sun in hot climates; ensure good air circulation to prevent fungal issues.
Care Requirements
Care Difficulty
very easyeasy
Sunlight
full sun
Rotate plants for even growth; use shade cloth in extreme heat; avoid placing in drafty areas.
Watering
every 7–10 days during active growth, less frequently in dormant periods
Water thoroughly but infrequently; ensure good drainage; avoid wetting foliage.
Soil
well-drained, sandy or loamy soil
pH: Slightly acidic to neutral (pH 6.0–7.0).
Avoid waterlogged soil; ensure good aeration; amend with compost if needed.
Temperature
Prefers cool to moderate temperatures (60–75°F or 15–24°C); can tolerate cooler nights.
Avoid sudden temperature fluctuations; protect from frost; ensure good air circulation.
Fertilizing
rarely required, if at all, due to its wild nature
Use a low-nitrogen fertilizer; fertilize sparingly; apply before active growth begins.
Propagation
Methods
Seed propagation is the primary method; direct sow in fall or early spring.
Step-by-Step Propagation Guide
- Sow seeds directly in the garden.
- Thin seedlings to desired spacing.
- Water lightly until established.
Best Time: Early spring or fall when temperatures are moderate.
Environment
Full sun; well-drained soil; moderate moisture.
Medium
Well-draining soil mix; can be sown directly in the garden.
Hormone
Not required for seed propagation.
Timeline
Germination in 7–14 days; plants reach maturity in 2–3 months.
Tools Needed
Garden trowel, watering can, seed tray (optional).
Quick Tips
Sow seeds in groups for better germination; keep soil consistently moist but not waterlogged.
Pruning & Repotting
Pruning Guide
Method
Snip off damaged stems at the base; no specific techniques needed.
Pruning Plan
Not typically required; remove dead or damaged stems if necessary.
Tools
Hand pruners or scissors.
Checklist
Inspect for damage; remove dead stems; clean tools after use.
Repotting Guide
Best Season
N/A
Pot Size
N/A
Method
N/A
Suggestions
Not applicable; Avena fatua is typically grown directly in the garden.
Checklist
N/A
Advanced Care Tips
Watering Mastery
Watering Checklist
Check soil moisture; water deeply; ensure drainage; avoid wetting leaves.
How to Apply Water Properly
Water at the base of the plant, ensuring moisture reaches the root zone; allow excess water to drain away; water early in the morning to minimize evaporation.
Watering Schedule Tips
Water deeply once the top inch of soil is dry; reduce frequency in winter to prevent root rot.
Soil Improvement
Add organic matter like compost to improve fertility and drainage; ensure soil is not compacted.
Temperature Stress Management
Signs of Temperature Issues
Wilting, yellowing leaves, or stunted growth in extreme heat; browning leaf tips in cold stress.
Cold Stress
Slows growth and seed development; may cause leaf discoloration or dieback in prolonged cold.
Solution: Provide frost protection in cold climates; avoid overwatering in cool conditions to prevent root rot.
Hot Stress
Can lead to premature flowering and seed shattering; may cause leaf scorch or wilting.
Solution: Provide afternoon shade in hot climates; maintain consistent soil moisture; use mulch to retain soil coolness.
Fertilizing Guide
Fertilizing Checklist
Use balanced fertilizer; apply in early spring; avoid over-fertilization.
Fertilizing Method
Lightly fertilize with a balanced, slow-release fertilizer in early spring; avoid excessive nitrogen to prevent lodging.
Common Problems & Solutions
Toxicity Warning
Cats
Non-toxicAvena fatua is not toxic to cats. The plant does not pose a risk of poisoning to felines.
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Dogs
Non-toxicAvena fatua is not toxic to dogs. The plant does not contain compounds that are harmful to canines.
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Humans
Non-toxicAvena fatua, commonly known as wild oat, is not considered toxic to humans under normal circumstances. It is primarily an agricultural weed but does not pose significant health risks.
⚡ Toxic If:
Generally non-toxic
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: Is Wild Oat edible?
A: While related to cultivated oats, Wild Oat is generally not recommended for consumption due to potential toxicity and lower nutritional quality compared to domesticated varieties.
Q: How can I control Wild Oat in my garden?
A: Manual removal, mowing before seed set, or using selective herbicides are effective methods to manage this weed.
Q: Does Wild Oat attract wildlife?
A: Yes, it provides habitat and food for various wildlife, including birds and small mammals, and can support pollinators.
Quick Reference
| Family: | Poaceae |
| Care: | very easy |
| Light: | full sun |
| Water: | every 7–10 days during activ |
Get Expert Care Tips
Download the Plantious app for personalized care reminders and plant identification!
Google Play App Store